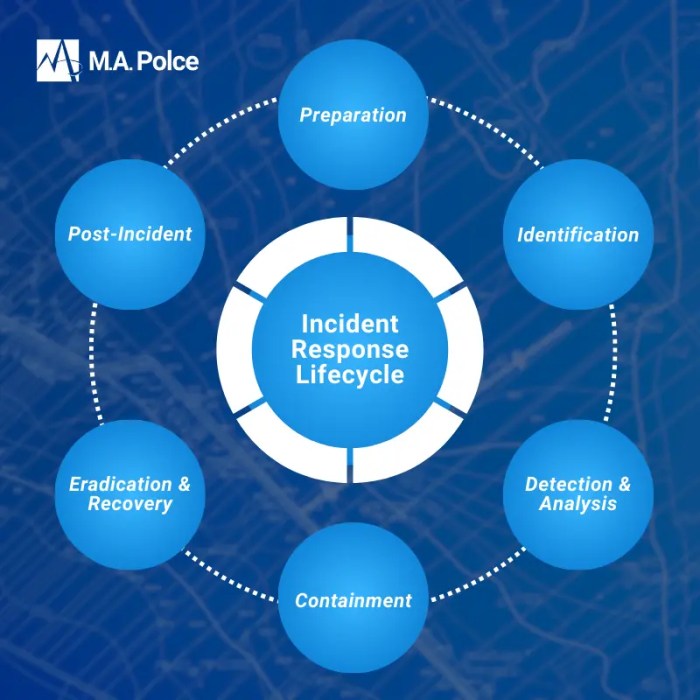
In today’s digital landscape, where cyber threats constantly evolve, the need for robust security measures is paramount. While technological solutions are crucial, they are only one piece of the puzzle. The human element remains a significant vulnerability. This guide explores how to implement security awareness training for employees, transforming your workforce into a proactive line of defense against cyberattacks.
This comprehensive overview will navigate the essential steps involved in creating and deploying an effective security awareness training program. From understanding the importance of training and identifying target audiences to choosing the right platform and measuring its impact, we will delve into practical strategies to empower your employees and safeguard your organization.
Understanding the Importance of Security Awareness Training
Security awareness training is no longer a luxury; it’s a necessity for organizations of all sizes in today’s threat landscape. Human error remains a significant factor in cybersecurity breaches, making a well-trained workforce the first line of defense. This training empowers employees to recognize and respond to threats, safeguarding sensitive data and critical assets.
Core Reasons for Security Awareness Training
Effective security awareness training is crucial for protecting an organization from a variety of threats. It transforms employees from potential vulnerabilities into informed defenders.
- Mitigating Human Error: The most common cause of data breaches is human error, such as falling for phishing scams, using weak passwords, or misconfiguring systems. Training equips employees with the knowledge and skills to avoid these pitfalls.
- Protecting Sensitive Data: Organizations handle vast amounts of sensitive information, including customer data, financial records, and intellectual property. Training helps employees understand the importance of data security and how to protect it from unauthorized access.
- Reducing Financial Losses: Data breaches can lead to significant financial losses due to incident response costs, legal fees, regulatory fines, and reputational damage. Training helps to prevent these costly incidents.
- Ensuring Compliance: Many industries are subject to regulations that require security awareness training, such as HIPAA, GDPR, and PCI DSS. Training helps organizations meet these compliance requirements and avoid penalties.
- Building a Security Culture: Training fosters a security-conscious culture within the organization, where security is everyone’s responsibility. This proactive approach helps to identify and address vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
Real-World Security Breaches Preventable Through Training
Many real-world security breaches could have been avoided or mitigated with effective security awareness training. These examples highlight the importance of training in various scenarios.
- Phishing Attacks: In 2022, phishing attacks were the most common initial access vector for cyberattacks. An employee clicking a malicious link or providing credentials to a phishing email can lead to a full-scale breach. Effective training teaches employees to identify and report phishing attempts. For example, the 2015 breach of the U.S. Office of Personnel Management (OPM), which exposed the personal information of millions of federal employees, was partially attributed to successful phishing attacks.
- Password Security Failures: Weak or reused passwords are a common entry point for attackers. Training on password best practices, such as using strong, unique passwords and enabling multi-factor authentication, can prevent unauthorized access. The 2017 Equifax data breach, which compromised the personal information of over 147 million people, involved the exploitation of a known vulnerability that could have been mitigated with stronger password security.
- Social Engineering: Attackers often use social engineering techniques to manipulate employees into divulging sensitive information or performing actions that compromise security. Training on social engineering tactics, such as pretexting and baiting, helps employees recognize and resist these attacks. The 2014 Target data breach, which resulted in the theft of credit and debit card information from millions of customers, involved attackers gaining access to Target’s network through compromised credentials obtained via social engineering.
- Insider Threats: Employees, whether intentionally or unintentionally, can pose a security risk. Training on data handling procedures, acceptable use policies, and the importance of reporting suspicious activity helps to mitigate insider threats.
Benefits of a Security-Aware Workforce
A security-aware workforce provides numerous benefits to an organization, leading to a stronger security posture and improved overall performance.
- Reduced Risk of Data Breaches: A well-trained workforce is less likely to fall victim to phishing scams, social engineering attacks, and other threats, reducing the risk of costly data breaches.
- Improved Compliance: Security awareness training helps organizations meet regulatory requirements and avoid penalties for non-compliance.
- Enhanced Reputation: Demonstrating a commitment to data security through training can enhance an organization’s reputation and build trust with customers and stakeholders.
- Increased Employee Productivity: A secure environment reduces the likelihood of downtime and disruptions caused by security incidents, leading to increased employee productivity.
- Cost Savings: Preventing data breaches and security incidents can save organizations significant amounts of money on incident response costs, legal fees, and regulatory fines.
- Stronger Security Culture: A security-aware workforce fosters a culture of security, where employees are proactive in identifying and reporting potential threats. This collaborative approach enhances the organization’s overall security posture.
Identifying Target Audiences and Tailoring Training

To maximize the effectiveness of security awareness training, it’s crucial to understand that a “one-size-fits-all” approach is rarely successful. Different employee groups have varying levels of technical expertise and face different threats. Therefore, tailoring training content to specific roles and responsibilities is essential for engagement and knowledge retention. This approach ensures that employees receive relevant information, making the training more impactful and practical.
Segmenting Employees Based on Roles and Responsibilities
Employees should be segmented into groups based on their roles and the associated security risks they face. This allows for the creation of targeted training modules that address specific vulnerabilities.For instance:
- Executive Leadership: This group often handles sensitive information and is a prime target for phishing attacks and social engineering. Their training should focus on recognizing sophisticated attacks, understanding their role in incident response, and protecting company reputation.
- IT Department: IT staff requires in-depth training on technical security controls, vulnerability management, incident response, and secure coding practices. They are the frontline defenders and need advanced knowledge.
- HR Department: HR professionals handle sensitive employee data, making them targets for data breaches and phishing attacks aimed at accessing personal information. Training should cover data privacy regulations, access control, and recognizing social engineering attempts.
- Finance Department: Finance employees manage financial transactions and are prime targets for fraud and financial scams. Training should emphasize fraud detection, secure payment processing, and recognizing phishing attempts targeting financial accounts.
- Sales and Marketing: This group often handles customer data and is susceptible to phishing, malware, and data leakage. Training should focus on data protection, secure communication, and recognizing social engineering attempts designed to steal customer information.
- Customer Service: Customer service representatives often interact with customers and may be targeted with social engineering attacks or requests for sensitive information. Training should cover identifying and reporting suspicious activities and protecting customer data.
- Remote Workers: With the rise of remote work, this group requires training on securing home networks, using VPNs, and protecting company data on personal devices.
Comparing and Contrasting Training Approaches for Different Departments
The training approach should vary depending on the department’s specific needs and responsibilities. This comparison highlights how to differentiate the training:
- IT Department: Training should be highly technical and in-depth. It should include hands-on exercises, simulations of attacks, and practical application of security tools and techniques. The focus is on building technical proficiency and understanding of security protocols. Training should be regularly updated to cover new threats and technologies.
- HR Department: Training should focus on data privacy regulations (e.g., GDPR, CCPA), access control, and recognizing social engineering attacks designed to obtain employee data. The training should emphasize practical scenarios and role-playing exercises to improve the ability to identify and respond to threats.
- Finance Department: Training should focus on fraud detection, secure payment processing, and recognizing phishing attempts targeting financial accounts. It should include case studies of financial scams and practical exercises to improve the ability to identify and report suspicious transactions.
- General Employees: For employees in other departments, the training should be more general, focusing on common threats like phishing, password security, and data protection. The training should be concise, engaging, and easy to understand. Regular refreshers and simulated phishing exercises are crucial.
Identifying Common Security Threats Faced by Each Employee Group
Understanding the common security threats faced by each employee group is crucial for tailoring the training effectively. Here’s a breakdown:
- Executive Leadership:
- Phishing attacks: Spear phishing and business email compromise (BEC) are common threats.
- Social engineering: Attacks aimed at gaining access to sensitive information or influencing decisions.
- Data breaches: Risk of exposure of confidential company data.
- IT Department:
- Malware and ransomware: Targeted attacks to disrupt systems and steal data.
- Vulnerability exploitation: Exploiting weaknesses in software and hardware.
- Insider threats: Malicious or negligent actions by IT staff.
- HR Department:
- Phishing attacks: Attempts to steal employee data.
- Data breaches: Exposure of sensitive employee information.
- Social engineering: Attempts to gain access to HR systems or influence employee actions.
- Finance Department:
- Phishing attacks: Targeting financial accounts and transactions.
- Fraud and financial scams: Attempts to steal money or assets.
- Business email compromise (BEC): Impersonation of executives to authorize fraudulent payments.
- Sales and Marketing:
- Phishing attacks: Targeting customer data and accounts.
- Data leakage: Accidental or intentional exposure of customer information.
- Malware: Infection through malicious links or attachments.
- Customer Service:
- Social engineering: Attempts to obtain sensitive customer information.
- Phishing attacks: Targeting customer accounts.
- Data breaches: Exposure of customer data through compromised accounts.
- Remote Workers:
- Phishing attacks: Targeting home networks and personal devices.
- Malware: Infection through unsecured home networks.
- Data breaches: Exposure of company data on personal devices.
Developing Training Content
Creating effective security awareness training hinges on the development of engaging and informative content. The content must cover a range of essential topics, delivered through diverse formats, and incorporate interactive elements to ensure knowledge retention and behavioral change. This section Artikels the key components necessary for a successful security awareness training program.
Essential Security Awareness Training Topics
A comprehensive security awareness training program must address several critical areas to equip employees with the knowledge and skills needed to protect themselves and the organization from cyber threats. Focusing on these topics provides a strong foundation for a security-conscious culture.
- Phishing Awareness: Phishing attacks are a primary method for cybercriminals to gain access to sensitive information. Training should cover:
- Identifying phishing emails: Recognizing suspicious sender addresses, generic greetings, urgent requests, and links to unfamiliar websites.
- Understanding phishing tactics: Learning about various phishing techniques, including spear phishing (targeted attacks), whaling (targeting high-profile individuals), and smishing (SMS phishing).
- Reporting phishing attempts: Knowing how to report suspicious emails and messages to the appropriate security team or IT department.
- Password Security: Weak passwords are a significant vulnerability. Training should focus on:
- Creating strong passwords: Emphasizing the use of long, complex passwords with a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Password management: Recommending the use of password managers to securely store and manage multiple passwords.
- Avoiding password reuse: Highlighting the risks of using the same password across multiple accounts.
- Social Engineering: Social engineering exploits human psychology to manipulate individuals into divulging confidential information or performing actions that compromise security. Training should cover:
- Understanding social engineering tactics: Recognizing common techniques such as impersonation, pretexting, and baiting.
- Identifying social engineering attempts: Learning to identify suspicious requests, unexpected phone calls, and unsolicited emails.
- Protecting against social engineering: Practicing critical thinking and verifying requests before taking action.
- Malware and Ransomware: Malware and ransomware pose significant threats to data and system integrity. Training should include:
- Understanding malware types: Learning about different types of malware, including viruses, worms, Trojans, and spyware.
- Recognizing malware symptoms: Identifying signs of malware infection, such as slow computer performance, unexpected pop-ups, and unusual file activity.
- Preventing malware infections: Emphasizing the importance of keeping software updated, avoiding suspicious websites, and exercising caution when opening attachments or clicking links.
- Ransomware specifics: Educating about the nature of ransomware, the risks of paying ransoms, and data backup strategies.
- Data Privacy and Protection: Protecting sensitive data is crucial for compliance and maintaining trust. Training should cover:
- Understanding data classification: Learning how to classify data based on its sensitivity and importance.
- Data handling procedures: Following established procedures for storing, accessing, and sharing sensitive data.
- Protecting personal information: Recognizing and complying with privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA.
- Physical Security: Physical security measures are essential to protect assets and prevent unauthorized access. Training should include:
- Securing physical devices: Protecting laptops, smartphones, and other devices from theft or loss.
- Access control: Following procedures for badge access, visitor management, and secure areas.
- Workplace security: Reporting suspicious activity and maintaining a secure work environment.
- Incident Reporting: Prompt reporting of security incidents is critical for effective response and mitigation. Training should cover:
- Identifying security incidents: Recognizing potential security breaches, such as data leaks, unauthorized access, and suspicious activity.
- Reporting procedures: Knowing how to report incidents to the appropriate channels within the organization.
- Incident response: Understanding the organization’s incident response plan and the steps involved in addressing security breaches.
Training Formats and Delivery Methods
Delivering security awareness training through various formats can enhance engagement and cater to different learning styles. Combining different methods maximizes the impact of the training program.
- Online Modules: Online modules offer a flexible and scalable way to deliver training.
- Advantages: Cost-effective, accessible anytime, anywhere, and easily updated.
- Content: Incorporate videos, interactive quizzes, and real-world examples.
- Examples: Use platforms like KnowBe4 or Proofpoint to create and deliver engaging online modules.
- In-Person Workshops: In-person workshops provide opportunities for direct interaction and discussion.
- Advantages: Facilitate hands-on activities, promote collaboration, and allow for immediate feedback.
- Activities: Include group discussions, case studies, and role-playing exercises.
- Example: Conduct a phishing simulation exercise where employees identify and report a simulated phishing email.
- Gamified Experiences: Gamification can make security awareness training more engaging and memorable.
- Advantages: Increase motivation, improve knowledge retention, and foster a competitive environment.
- Methods: Incorporate quizzes, leaderboards, and points-based systems.
- Examples: Use gamified platforms or create custom games to test employee knowledge of security best practices.
- Simulations and Simulations Exercises: Simulating real-world scenarios helps employees apply their knowledge and skills.
- Phishing Simulations: Send simulated phishing emails to assess employee awareness and identify vulnerabilities.
- Password Cracking Exercises: Demonstrate the ease with which weak passwords can be compromised.
- Social Engineering Scenarios: Present realistic social engineering scenarios to test employee responses.
Interactive Elements and Assessments
Integrating interactive elements and assessments into training programs reinforces learning and measures effectiveness. These elements help to ensure that the training resonates with the audience and drives behavioral change.
- Interactive Quizzes: Quizzes test understanding and provide immediate feedback.
- Types: Include multiple-choice questions, true/false questions, and scenario-based questions.
- Benefits: Reinforce key concepts and identify areas for improvement.
- Example: Include a quiz at the end of each training module to assess comprehension.
- Scenario-Based Exercises: Scenario-based exercises allow employees to apply their knowledge in realistic situations.
- Methods: Present scenarios that require employees to make decisions based on security best practices.
- Benefits: Enhance critical thinking skills and promote practical application of knowledge.
- Example: Present a scenario where an employee receives a suspicious email and asks them to identify the potential risks and appropriate actions.
- Real-World Examples: Real-world examples illustrate the impact of security breaches and the importance of following security protocols.
- Sources: Use case studies, news articles, and internal incident reports.
- Benefits: Make the training more relatable and demonstrate the consequences of security failures.
- Example: Share a case study of a company that suffered a data breach due to a phishing attack.
- Assessments: Conduct periodic assessments to measure the effectiveness of the training program.
- Methods: Include pre- and post-training assessments, regular quizzes, and phishing simulations.
- Metrics: Track employee knowledge, changes in behavior, and the reduction of security incidents.
- Example: Compare the results of a pre-training assessment to a post-training assessment to evaluate the impact of the training program.
Choosing the Right Training Platform and Tools
Selecting the appropriate security awareness training platform is crucial for the success of your program. The right platform should align with your organization’s specific needs, budget, and technical capabilities. Careful consideration of various factors, from features and ease of use to integration capabilities, will ensure a smooth implementation and effective training delivery.
Selection Criteria for a Security Awareness Training Platform
Establishing clear selection criteria is the first step in choosing the right platform. This process helps narrow down options and ensures the chosen platform meets your organization’s requirements.
- Features: Identify the essential features required. This includes the types of training modules offered (e.g., phishing simulations, video-based training, interactive quizzes), reporting and analytics capabilities, and customization options. Consider if the platform offers a content library that is updated regularly with the latest threats and attack vectors.
- Cost: Determine your budget. Training platform pricing models vary, from per-user licenses to subscription-based models. Consider the total cost of ownership, including initial setup fees, ongoing maintenance, and potential add-ons. Factor in the value provided by the platform and whether it aligns with your budget constraints.
- Ease of Use: Assess the platform’s user-friendliness for both administrators and employees. A platform with an intuitive interface and straightforward navigation will facilitate easier management and encourage higher employee engagement. Evaluate the availability of training resources and support documentation.
- Integration Capabilities: Determine the platform’s ability to integrate with existing HR systems, such as your Learning Management System (LMS) and Single Sign-On (SSO) providers. Seamless integration streamlines user management and simplifies training assignment and tracking.
- Content Quality and Relevance: Evaluate the quality and relevance of the training content. The content should be engaging, up-to-date, and aligned with industry best practices and your organization’s specific security policies. Look for platforms that offer localized content or the ability to customize training materials.
- Reporting and Analytics: The platform should provide comprehensive reporting and analytics to track training progress, identify areas of weakness, and measure the effectiveness of the training program. Key metrics to consider include completion rates, phishing simulation results, and knowledge assessment scores.
- Support and Customer Service: Consider the level of support and customer service provided by the platform vendor. This includes access to technical support, training resources, and a dedicated account manager. Reliable support is crucial for resolving issues and ensuring a positive user experience.
Comparison Table of Popular Training Platforms
The following table provides a comparison of several popular security awareness training platforms, highlighting key features and pricing information. Note that pricing can vary based on the number of users and the specific features selected. This table is for illustrative purposes and is based on publicly available information. It is always recommended to get direct quotes from vendors for the most accurate pricing.
| Platform | Key Features | Pricing (Approximate) | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KnowBe4 | Phishing simulations, training modules, automated campaigns, reporting and analytics. Offers a vast library of content. | Per-user, per-year. Varies based on the package and features selected. Starts around $25/user/year. | Comprehensive feature set, easy to use, strong reporting. | Can be expensive for large organizations. |
| Proofpoint Security Awareness Training | Phishing simulations, training modules, advanced threat intelligence integration, risk scoring. | Per-user, per-year. Pricing varies. | Strong focus on threat intelligence and advanced simulations. | Can be complex to set up and manage. |
| SANS Security Awareness Training | Training modules, phishing simulations, customizable content, assessment tools. Offers content from the SANS Institute. | Per-user, per-year. Pricing varies. | High-quality content, reputable brand. | Can be less flexible than other platforms. |
| Cofense | Phishing simulation, reporting and analytics, incident response, and phishing email analysis. | Per-user, per-year. Pricing varies. | Strong focus on phishing simulation and incident response. | Can be expensive. |
| Barracuda Phishing Simulation and Training | Phishing simulations, training modules, reporting and analytics. Offers a range of templates. | Per-user, per-year. Pricing varies. | Easy to set up and use, cost-effective. | Content library is less extensive compared to some other platforms. |
Integrating Training Platforms with Existing HR Systems
Integrating your chosen security awareness training platform with existing HR systems can significantly streamline the training process. This integration can automate user provisioning, training assignment, and progress tracking, reducing administrative overhead and improving efficiency.
- Single Sign-On (SSO) Integration: Implement SSO to allow employees to access the training platform using their existing credentials. This eliminates the need for separate logins and simplifies user access. Many platforms support popular SSO providers such as Microsoft Azure Active Directory, Okta, and Google Workspace.
- Learning Management System (LMS) Integration: Integrate the training platform with your LMS to centralize training management. This allows you to assign training, track completion rates, and generate reports from a single system. Many platforms offer integrations with popular LMS systems like Cornerstone, Workday, and Moodle.
- Automated User Provisioning: Automate user provisioning by synchronizing user data from your HR system to the training platform. This ensures that new employees are automatically added to the platform and assigned the appropriate training modules. This is often achieved through API integrations or CSV file uploads.
- Data Synchronization: Establish data synchronization between the training platform and your HR system to keep user data consistent. This includes updates to user profiles, job titles, and department assignments. This ensures that training assignments and reporting are accurate.
- API Integration: Utilize APIs to integrate the training platform with your HR system. APIs allow for automated data exchange, enabling features like user provisioning, training assignment, and progress tracking. This approach often offers the most flexibility and customization options.
Implementing a Security Awareness Training Program
Launching a security awareness training program effectively requires a structured approach. This involves careful planning, clear communication, and ongoing reinforcement to ensure employees understand and internalize security best practices. This section Artikels a step-by-step procedure for implementing a successful program.
Step-by-Step Procedure for Launching a Security Awareness Training Program
Implementing a security awareness training program requires a systematic approach to ensure its effectiveness. This process involves several key stages, from initial planning to ongoing evaluation.
- Planning and Preparation: This initial phase sets the foundation for the entire program.
- Define Objectives and Scope: Clearly Artikel the goals of the training. What specific security risks are you trying to mitigate? Determine which departments and roles the training will cover. Consider legal and compliance requirements.
- Assemble a Training Team: Form a team including representatives from IT, HR, legal, and relevant business units. This ensures diverse perspectives and support for the program.
- Budget Allocation: Allocate a budget for training materials, platform licenses, and potentially, external training providers.
- Policy Review and Updates: Review and update existing security policies to align with the training content. Ensure policies are easily accessible to employees.
- Select or Develop Training Content: Based on the needs assessment, choose pre-built training modules or create custom content. Tailor the content to your industry, organization size, and employee roles.
- Incorporate Organizational Examples: Use examples of past security incidents or near misses within your organization. This makes the training more relevant and impactful.
- Translate and Localize: If your workforce is multilingual, translate training materials into relevant languages. Consider cultural nuances to ensure effective communication.
- Select a Training Platform: Choose a Learning Management System (LMS) or other platform that meets your needs. Consider features like automated enrollment, progress tracking, and reporting.
- Configure the Platform: Set up user accounts, upload training modules, and configure assessments.
- Testing: Conduct thorough testing of the training modules and platform functionality to ensure a smooth user experience.
- Announce the Program: Inform employees about the training program through various channels, such as email, newsletters, and company meetings.
- Highlight Benefits: Explain the benefits of the training to employees, such as protecting themselves and the company from cyber threats.
- Provide Access and Instructions: Clearly communicate how employees can access the training materials and the expected completion deadlines.
- Launch Training: Make the training available to employees according to the established schedule.
- Deliver Training: Ensure employees complete the training modules. Consider a variety of training formats, such as online modules, webinars, and in-person sessions.
- Monitor Progress: Track employee completion rates and assessment scores. Identify employees who are not completing the training.
- Provide Support: Offer technical support and answer employee questions. Provide resources for employees who need additional help.
- Conduct Assessments: Use quizzes, simulations, and other assessments to evaluate employee understanding of the material.
- Gather Feedback: Collect feedback from employees about the training program. Use surveys and focus groups to identify areas for improvement.
- Analyze Results: Analyze assessment results and feedback to identify areas where the training was effective and areas that need improvement.
- Provide Ongoing Reinforcement: Send regular security tips and reminders to employees. Conduct phishing simulations and other exercises to reinforce learning.
- Update Training Content: Regularly update training content to reflect changes in the threat landscape and organizational policies.
- Iterate and Improve: Based on assessment results and feedback, make adjustments to the training program. Consider adding new modules or modifying existing content.
Best Practices for Communicating the Program to Employees and Gaining Buy-in
Effective communication is crucial for gaining employee buy-in and ensuring the success of a security awareness training program. The following best practices can help achieve this.
- Emphasize the “Why”: Clearly explain the reasons for the training. Focus on the benefits to employees and the organization. Highlight the potential consequences of security breaches, such as financial losses, reputational damage, and personal data exposure.
- Use Multiple Communication Channels: Communicate the program through various channels, including email, newsletters, company meetings, intranet announcements, and posters. This ensures that all employees are aware of the training.
- Gain Leadership Support: Obtain support from senior management and department heads. Their endorsement demonstrates the importance of the training and encourages employee participation. Have leaders participate in the training themselves.
- Make it Relevant: Tailor the training content to the specific risks faced by the organization and the roles of employees. Use examples that are relevant to their daily work.
- Make it Engaging: Use interactive training methods, such as quizzes, simulations, and gamification, to keep employees engaged. Avoid overly technical jargon and use clear, concise language.
- Address Concerns: Be prepared to answer employee questions and address any concerns they may have about the training. Provide clear and concise answers.
- Offer Incentives: Consider offering incentives for completing the training, such as recognition, rewards, or opportunities for professional development.
- Be Consistent: Regularly communicate security tips and reminders to reinforce the training. Consistency helps keep security awareness top of mind.
Timeline for Training Delivery, Including Initial Training and Ongoing Reinforcement
Creating a well-defined timeline for training delivery is essential for ensuring the program’s effectiveness. This timeline should include both initial training and ongoing reinforcement activities.
- Phase 1: Pre-Launch (4-6 Weeks Before Launch)
- Weeks 4-6: Announce the upcoming training program to employees. This can be done through email announcements, company newsletters, and intranet postings. Provide a brief overview of the program and its benefits.
- Weeks 2-3: Send more detailed information about the training, including the topics covered, the platform used, and the expected completion date. Highlight the importance of the training and encourage employee participation.
- Week 1: Send a final reminder before the training launch. Provide clear instructions on how to access the training and answer any remaining questions.
- Week 1: Launch the training program. Provide employees with access to the training modules and set a clear deadline for completion. Monitor completion rates and send reminders to employees who have not yet completed the training.
- Weeks 2-4: Continue to monitor completion rates and send reminders. Provide support to employees who have questions or are experiencing technical difficulties. Analyze initial assessment results to identify areas where employees are struggling.
- Monthly: Send regular security awareness newsletters or emails with tips, reminders, and updates on the latest threats. Share examples of real-world phishing attempts and other security incidents.
- Quarterly: Conduct phishing simulations to test employee awareness and identify areas for improvement. Analyze the results and provide feedback to employees. Update training content to reflect changes in the threat landscape.
- Annually: Require employees to complete a refresher training course. Review and update security policies. Conduct a comprehensive assessment of the program’s effectiveness.
Example: A retail company with 5,000 employees implemented a security awareness training program. The initial training was launched over a two-week period, with a mandatory completion deadline. They then sent monthly security newsletters and conducted quarterly phishing simulations. After one year, they reported a 40% reduction in successful phishing attacks and a significant improvement in employee awareness of security threats.
Measuring Training Effectiveness and ROI
Effectively measuring the impact of security awareness training is crucial for demonstrating its value and justifying continued investment. This involves tracking key performance indicators (KPIs), collecting employee feedback, and analyzing the data to identify areas for improvement. A well-defined measurement strategy ensures the training program remains relevant, engaging, and ultimately, successful in mitigating security risks.
Methods for Measuring Training Effectiveness
Several methods can be employed to gauge the effectiveness of security awareness training. These methods, when used in combination, provide a comprehensive view of the training’s impact.
- Pre- and Post-Training Assessments: Administering assessments before and after the training is a fundamental approach. These assessments can be in the form of quizzes, surveys, or simulated scenarios. By comparing the results, organizations can directly measure the knowledge gained and behavioral changes among employees. For example, a pre-training quiz might reveal that 30% of employees are unaware of phishing tactics. Post-training, this figure might drop to 5%, indicating a significant improvement.
- Phishing Simulations: Regularly conducting simulated phishing attacks is a practical way to assess employee vigilance. Tracking click-through rates on these simulations provides valuable data on how effectively employees are recognizing and avoiding phishing attempts. A decrease in click-through rates over time signifies improved awareness.
- Observation and Analysis of Security Incidents: Monitoring the frequency and nature of security incidents, such as data breaches or malware infections, before and after the training can reveal the program’s effectiveness. A reduction in these incidents suggests that the training is positively influencing employee behavior and reducing risks.
- Review of Employee Reporting: Assessing the frequency and quality of employee reporting of suspicious activities, such as phishing emails or unusual network behavior, provides insights into the impact of training. An increase in the volume and accuracy of reports indicates improved awareness and willingness to participate in security efforts.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to Track
Tracking the right KPIs is essential for accurately measuring the impact of security awareness training. These metrics provide tangible data to assess the program’s success and identify areas for improvement.
- Click-Through Rates on Phishing Simulations: This is a critical KPI, directly reflecting employee susceptibility to phishing attacks. A decreasing click-through rate indicates improved ability to identify and avoid phishing attempts. For instance, if initial click-through rates are 25%, a successful training program might reduce this to below 5% within a year.
- Password Strength: Measuring the average strength of employee passwords before and after training is another key indicator. Tools can be used to assess password complexity, length, and the use of unique passwords across different accounts. Improved password practices reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
- Reporting of Suspicious Emails and Activities: The number of suspicious emails and activities reported by employees reflects their awareness and willingness to engage in security practices. An increase in reports, especially those validated as legitimate threats, indicates improved recognition of potential risks.
- Completion Rates and Scores on Training Modules: Monitoring the completion rates and scores on training modules ensures employees are actively participating and understanding the material. Low completion rates or poor scores indicate potential issues with the training content or delivery method.
- Reduction in Security Incidents: Tracking the frequency and impact of security incidents, such as data breaches or malware infections, provides a direct measure of the training’s effectiveness in mitigating risks. A decrease in the number and severity of incidents indicates a successful program.
- Employee Feedback and Surveys: Gathering employee feedback through surveys or other methods helps assess the training’s relevance, engagement, and overall effectiveness. Positive feedback can identify areas where the training resonates, while negative feedback highlights areas needing improvement.
Designing a System for Collecting Employee Feedback and Making Improvements
Establishing a robust feedback mechanism is crucial for continuously improving the security awareness training program. This involves creating multiple channels for employees to provide input and incorporating their feedback into the training content and delivery.
- Regular Surveys: Conduct periodic surveys to gather employee feedback on the training’s content, delivery, and overall effectiveness. Surveys can be anonymous to encourage honest responses. Use a variety of question types, including multiple-choice, rating scales, and open-ended questions.
- Feedback Forms: Provide easily accessible feedback forms where employees can submit comments, suggestions, and report any issues they encounter. These forms should be easily accessible through the training platform, intranet, or other communication channels.
- Focus Groups: Organize focus groups to gather in-depth feedback from a representative sample of employees. This allows for more detailed discussions and the exploration of specific topics.
- Review of Training Materials: Establish a process for regularly reviewing and updating training materials based on feedback, emerging threats, and changes in the organization’s security policies. This includes reviewing the content, format, and delivery methods.
- Analysis of Feedback Data: Analyze the collected feedback data to identify common themes, trends, and areas for improvement. Use the data to prioritize changes and measure the impact of implemented improvements. For example, if surveys reveal that employees find a particular module confusing, revise the module to improve clarity and comprehension.
- Iterative Improvement: Implement an iterative improvement process, where changes are made to the training program based on feedback and data analysis, and then the impact of those changes is re-evaluated. This continuous cycle of feedback, improvement, and re-evaluation ensures the training program remains relevant and effective.
Phishing Simulations and Testing Employee Behavior
Phishing simulations are a crucial component of a comprehensive security awareness training program. They allow organizations to proactively test employee susceptibility to phishing attacks and identify areas where additional training and reinforcement are needed. By simulating real-world phishing attempts, companies can gauge the effectiveness of their training efforts and improve their overall security posture.
Designing and Implementing Phishing Simulations
Implementing effective phishing simulations requires careful planning and execution. The goal is to mimic real-world phishing attacks as closely as possible while remaining ethical and compliant with privacy regulations.
- Define Objectives: Clearly Artikel the goals of the simulation. Are you primarily testing click rates, data submission, or reporting behavior? Defining objectives will help you measure success.
- Choose a Simulation Platform: Several platforms automate phishing simulations, offering features like template libraries, automated reporting, and integration with training modules. Popular platforms include KnowBe4, Proofpoint, and PhishingBox. Select a platform that meets your specific needs and budget.
- Develop Realistic Scenarios: The more realistic the simulation, the more valuable the results.
- Consider Current Threats: Base simulations on current phishing trends. For example, attacks impersonating HR, IT support, or executives are common.
- Use Relevant Context: Tailor the simulated emails to your organization. Use internal branding, employee names, and current events to increase the likelihood of engagement.
- Craft Compelling Subject Lines: Subject lines are critical. Use urgency, curiosity, or personalization to grab attention.
- Design Realistic Landing Pages: If the simulation includes a link, create a realistic landing page that mimics a legitimate login portal or website.
- Segment Your Audience: Consider segmenting employees based on roles, departments, or past training performance. This allows you to tailor simulations and measure the effectiveness of training across different groups.
- Schedule and Frequency: Determine the frequency of simulations. Monthly or quarterly simulations are common. Schedule simulations at various times to capture different employee behaviors.
- Communicate Beforehand (Optional): Some organizations choose to announce the simulations beforehand, emphasizing that it is a learning exercise. Others prefer a surprise approach to gauge natural behavior.
- Track Metrics: Key metrics to track include:
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): The percentage of employees who click on the phishing link.
- Data Submission Rate: The percentage of employees who submit sensitive information (e.g., usernames, passwords).
- Reporting Rate: The percentage of employees who report the phishing attempt.
- Provide Feedback and Remediation: After each simulation, provide feedback to employees.
- Immediate Feedback: Redirect employees who click on a link to a training module or awareness page.
- Post-Simulation Report: Share a summary of the simulation results with employees, highlighting common mistakes and providing tips for avoiding future attacks.
- Iterate and Improve: Use the results of each simulation to refine your training program and improve future simulations. Continuously analyze trends and adapt to evolving phishing tactics.
Examples of Different Phishing Scenarios and Their Potential Impact
Phishing attacks come in many forms, each with the potential for significant damage. Understanding the different types of phishing scenarios and their potential impact is critical for effective security awareness training.
- Credential Harvesting:
- Scenario: An email impersonates the IT department, requesting employees to update their password by clicking on a link. The link leads to a fake login page that steals their credentials.
- Impact: Compromised credentials can lead to unauthorized access to sensitive data, financial fraud, and malware infections.
- Malware Delivery:
- Scenario: An email appears to be from a trusted source, such as a vendor or colleague, and contains a malicious attachment (e.g., a PDF or Word document) or a link to download malware.
- Impact: Malware can infect computers, steal data, encrypt files (ransomware), and spread throughout the network.
- Spear Phishing:
- Scenario: A highly targeted attack that uses personalized information to trick a specific individual or group into taking action. For example, an email impersonates a senior executive and requests an urgent wire transfer.
- Impact: Spear phishing attacks are often very successful due to their personalized nature. They can lead to significant financial losses, data breaches, and reputational damage.
- Business Email Compromise (BEC):
- Scenario: Attackers compromise a business email account and use it to impersonate the account owner, requesting fraudulent payments or sensitive information from colleagues or vendors.
- Impact: BEC attacks can result in substantial financial losses, disruption of business operations, and damage to the company’s reputation.
- Vishing (Voice Phishing):
- Scenario: An attacker calls an employee, pretending to be from a bank or IT support, and tries to trick them into revealing sensitive information or installing malware.
- Impact: Vishing can lead to financial losses, identity theft, and data breaches.
Detailed Report Summarizing the Results of a Phishing Simulation
Below is an example of an HTML report summarizing the results of a phishing simulation. This is a simplified example; actual reports from phishing simulation platforms will typically provide more detailed data and visualizations.
Phishing Simulation Report – October 26, 2023
Objective: Assess employee susceptibility to phishing attacks and identify areas for improvement in security awareness training.
Simulation Details:
- Subject: Urgent: Action Required – Password Update
- Sender: Security Team <[email protected]> (Spoofed)
- Target Audience: All Employees
- Link: <fake-login-page.example.com> (redirected to a training module)
Results:
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Total Employees Targeted | 500 |
| Emails Opened | 300 (60%) |
| Clicked on Link | 100 (33.3%) |
| Submitted Credentials | 5 (5%) |
| Reported Phishing Attempt | 25 (25%) |
Analysis:
The click-through rate of 33.3% indicates a moderate level of susceptibility to the phishing email. The low submission rate (5%) is positive, suggesting that most employees recognized the potential threat before entering their credentials. However, the reporting rate of 25% is concerning, indicating that many employees did not report the suspicious email.
Areas for Improvement:
- Reinforce training on recognizing phishing emails, particularly the importance of verifying sender addresses and scrutinizing links.
- Emphasize the importance of reporting suspicious emails, even if employees are unsure.
- Provide additional training on identifying and avoiding fake login pages.
Recommendations:
- Conduct refresher training on phishing awareness, focusing on the specific weaknesses identified in this simulation.
- Implement a more user-friendly reporting mechanism for suspicious emails.
- Consider sending a follow-up email to all employees, reiterating key phishing indicators and providing a link to additional resources.
Maintaining and Updating the Training Program

The cybersecurity landscape is constantly evolving, with new threats and vulnerabilities emerging regularly. A static security awareness training program quickly becomes outdated and ineffective. Therefore, maintaining and regularly updating your training program is crucial to ensuring your employees remain vigilant and protected against the latest cyber threats. This proactive approach helps to minimize risks and strengthens your organization’s overall security posture.
Importance of Regular Updates
Regularly updating your security awareness training program is paramount to its effectiveness. Cybercriminals are continuously developing new attack vectors, exploiting vulnerabilities, and refining their tactics. A training program that doesn’t adapt to these changes leaves employees vulnerable and the organization at risk. This adaptation ensures that the training remains relevant and addresses current threats, thereby maximizing its impact.
Checklist for Reviewing and Revising Training Content
To ensure your security awareness training remains effective, a structured approach to review and revision is essential. The following checklist provides a framework for this process:
- Frequency of Review: Establish a regular schedule for reviewing the training content. Consider quarterly or semi-annual reviews as a starting point, but adjust based on the organization’s risk profile and the frequency of significant security incidents or threat intelligence updates.
- Threat Landscape Analysis: Analyze the latest threat intelligence reports from reputable sources such as the Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), the SANS Institute, and industry-specific threat intelligence feeds. Identify new threats, vulnerabilities, and attack techniques relevant to your organization.
- Incident Review: Analyze any security incidents that have occurred within your organization. Identify the root causes of incidents, and determine if training content needs to be updated to address knowledge gaps or behavioral issues that contributed to the incidents.
- Content Audit: Conduct a thorough audit of all training materials, including presentations, videos, quizzes, and handouts. Verify the accuracy and relevance of the information presented.
- Relevance Assessment: Evaluate the relevance of the training content to your employees’ roles and responsibilities. Ensure that the content is tailored to the specific threats and risks they face in their daily work.
- Effectiveness Evaluation: Assess the effectiveness of the training program through post-training assessments, phishing simulations, and employee feedback. Identify areas where employees struggle or where the training could be improved.
- Content Updates: Based on the review, update the training content to reflect the latest threats, vulnerabilities, and best practices. This may involve adding new modules, revising existing content, or removing outdated information.
- Format and Delivery Updates: Ensure that the training materials are engaging and accessible to all employees. Consider updating the format and delivery methods to incorporate new technologies or approaches, such as interactive simulations or gamification.
- Communication and Feedback: Communicate the changes to the training program to all employees. Solicit feedback from employees to identify areas for improvement and ensure the training remains relevant and effective.
- Documentation and Version Control: Maintain detailed documentation of all updates and revisions to the training program. Implement a version control system to track changes and ensure that the latest version of the training materials is always available.
Methods for Staying Informed About Security Threats and Trends
Staying informed about the latest security threats and trends is essential for maintaining a relevant and effective security awareness training program. The following methods will assist in keeping abreast of the latest developments:
- Follow Reputable Security News Sources: Subscribe to industry-leading security news websites, blogs, and newsletters, such as those from SANS Institute, Krebs on Security, Threatpost, and Dark Reading. These sources provide timely updates on emerging threats, vulnerabilities, and attack techniques.
- Subscribe to Security Threat Intelligence Feeds: Utilize threat intelligence feeds from reputable security vendors, such as Recorded Future, CrowdStrike, and FireEye. These feeds provide real-time information on emerging threats, indicators of compromise (IOCs), and attack patterns.
- Participate in Industry Events and Conferences: Attend security conferences, webinars, and workshops to learn from industry experts and network with peers. Events such as RSA Conference, Black Hat, and DEF CON offer valuable insights into the latest security trends and best practices.
- Join Security Communities and Forums: Engage in online security communities and forums, such as Reddit’s r/netsec and the SANS ISC InfoSec Forums. These platforms provide opportunities to discuss security topics, share information, and learn from other security professionals.
- Follow Cybersecurity Experts and Influencers: Follow cybersecurity experts and thought leaders on social media platforms, such as Twitter and LinkedIn. These individuals often share valuable insights and updates on emerging threats and trends.
- Review Government and Industry Reports: Regularly review reports and advisories from government agencies, such as CISA, and industry organizations, such as the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). These resources provide valuable information on security best practices, threat assessments, and vulnerability disclosures.
- Conduct Regular Vulnerability Assessments and Penetration Testing: Perform regular vulnerability assessments and penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities in your organization’s systems and networks. These assessments provide valuable insights into the types of threats your organization faces and the effectiveness of your security controls.
- Encourage Employee Reporting: Establish a clear process for employees to report suspicious activity or potential security threats. This helps to identify and address threats quickly. Create a culture where employees feel comfortable reporting any potential issues.
Legal and Compliance Considerations
Security awareness training is not just a best practice; it’s often a legal and regulatory necessity. Organizations must understand and address the legal and compliance implications associated with data protection and privacy. This section explores the critical aspects of these considerations, emphasizing how effective security awareness training can help organizations meet their obligations.
Legal and Compliance Aspects Related to Security Awareness Training
Organizations operate within a complex web of legal and regulatory frameworks. Failing to comply with these regulations can result in significant penalties, including hefty fines, reputational damage, and legal action. Security awareness training is a crucial component in demonstrating a commitment to compliance.Some of the key regulations and compliance frameworks include:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): GDPR applies to organizations that process the personal data of individuals within the European Union (EU). It mandates that organizations implement appropriate technical and organizational measures to ensure a level of security appropriate to the risk. This includes security awareness training for all personnel who have access to personal data. Failure to comply can result in fines of up to €20 million or 4% of annual global turnover, whichever is higher.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA): HIPAA primarily affects healthcare providers and their business associates in the United States. It establishes standards for protecting sensitive patient health information (PHI). HIPAA requires organizations to train their workforce on the security and privacy of PHI. Non-compliance can lead to substantial financial penalties and criminal charges.
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) / California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA): These California laws grant consumers significant rights regarding their personal data. They require businesses to provide specific disclosures about data collection practices and to implement reasonable security measures to protect consumer data. Security awareness training is a key component of meeting the “reasonable security” requirements.
- Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS): PCI DSS applies to any organization that processes, stores, or transmits credit card information. While not a law, it’s a mandatory standard for businesses accepting card payments. PCI DSS includes requirements for security awareness training to educate employees about protecting cardholder data.
- Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX): SOX is primarily focused on financial reporting and internal controls for publicly traded companies in the United States. Although not directly related to cybersecurity, SOX requires organizations to maintain accurate financial records, which can be indirectly impacted by cybersecurity breaches. Robust security awareness training can help prevent financial fraud and data manipulation.
- Other Industry-Specific Regulations: Many other industries, such as finance, government, and education, have specific regulations that require security awareness training. These regulations often vary based on the sensitivity of the data and the potential risks.
How Security Awareness Training Helps Meet Regulatory Requirements
Effective security awareness training directly supports compliance with various regulations. It equips employees with the knowledge and skills to identify and mitigate security risks, thereby reducing the likelihood of data breaches and non-compliance.Here are specific examples of how security awareness training supports compliance:
- GDPR Compliance: Training on data protection principles, data subject rights, and how to handle personal data securely directly addresses GDPR requirements. For example, training might cover how to identify and respond to data subject access requests (DSARs) and how to report data breaches.
- HIPAA Compliance: Training on PHI security, privacy rules, and breach notification procedures ensures employees understand their responsibilities under HIPAA. This includes training on recognizing and avoiding phishing attempts, protecting patient data on mobile devices, and reporting potential HIPAA violations.
- CCPA/CPRA Compliance: Training on data privacy rights, data minimization, and security best practices helps organizations meet the “reasonable security” requirements of CCPA/CPRA. Training can focus on how to handle consumer data requests and prevent data breaches that could expose consumer information.
- PCI DSS Compliance: Training on PCI DSS requirements, such as protecting cardholder data, preventing phishing attacks, and recognizing social engineering attempts, helps organizations maintain compliance. This can include training on secure password practices, how to identify and report suspicious activities, and the importance of protecting cardholder data.
- Reducing the Risk of Data Breaches: By educating employees about common threats like phishing, malware, and social engineering, security awareness training helps reduce the likelihood of data breaches. Data breaches can lead to significant financial penalties and reputational damage, as well as legal liabilities.
- Demonstrating Due Diligence: Security awareness training provides evidence that an organization is taking reasonable steps to protect sensitive data. This is crucial in the event of a data breach or regulatory investigation. Training records and completion certificates can serve as proof of compliance efforts.
Resources and References for Further Reading
Staying informed about legal and compliance requirements is essential. Here are some resources and references for further reading on these topics:
- Official Regulatory Websites: The websites of regulatory bodies, such as the European Data Protection Board (EDPB) for GDPR, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) for HIPAA, and the California Attorney General’s Office for CCPA/CPRA, provide the most accurate and up-to-date information on regulations.
- Legal and Compliance Publications: Reputable legal and compliance publications, such as those from law firms specializing in data privacy and security, offer in-depth analysis and guidance on compliance requirements.
- Industry Associations: Organizations like the International Association of Privacy Professionals (IAPP) and the PCI Security Standards Council provide resources, certifications, and best practices for data privacy and security.
- Security Awareness Training Providers: Many security awareness training providers offer resources and guidance on legal and compliance topics, including white papers, webinars, and compliance checklists.
- Books and Academic Journals: Academic journals and books focusing on data privacy, cybersecurity law, and compliance offer in-depth analysis of the legal and regulatory landscape.
Final Wrap-Up
In conclusion, implementing security awareness training is not merely a compliance exercise; it’s an investment in your organization’s resilience. By equipping your employees with the knowledge and skills to recognize and respond to threats, you can significantly reduce your risk profile, improve compliance, and foster a security-conscious culture. Remember, a well-trained workforce is the strongest defense against the ever-present dangers of the digital world.
Embrace the strategies Artikeld here, and you’ll be well on your way to a safer and more secure future.
Questions and Answers
What is the ideal frequency for security awareness training?
Ideally, security awareness training should be conducted at least annually, with shorter, more frequent reinforcement activities like monthly newsletters, quizzes, or simulated phishing exercises to keep security top of mind.
How can I get buy-in from employees for security awareness training?
Communicate the “why” behind the training – explain the potential risks and how it protects them and the company. Make the training engaging and relevant to their roles. Offer incentives, recognize achievements, and involve employees in the process.
What are the key elements of a successful phishing simulation?
Successful phishing simulations should mimic real-world threats, use realistic scenarios, target different employee groups, and provide clear feedback and remediation after a simulated attack. Analyze the results to identify areas for improvement.
How do I measure the ROI of security awareness training?
Measure ROI by tracking metrics such as reduced click-through rates on phishing simulations, improved password security, fewer security incidents, and a decrease in data breaches. Compare these metrics before and after training.